Rottweiler
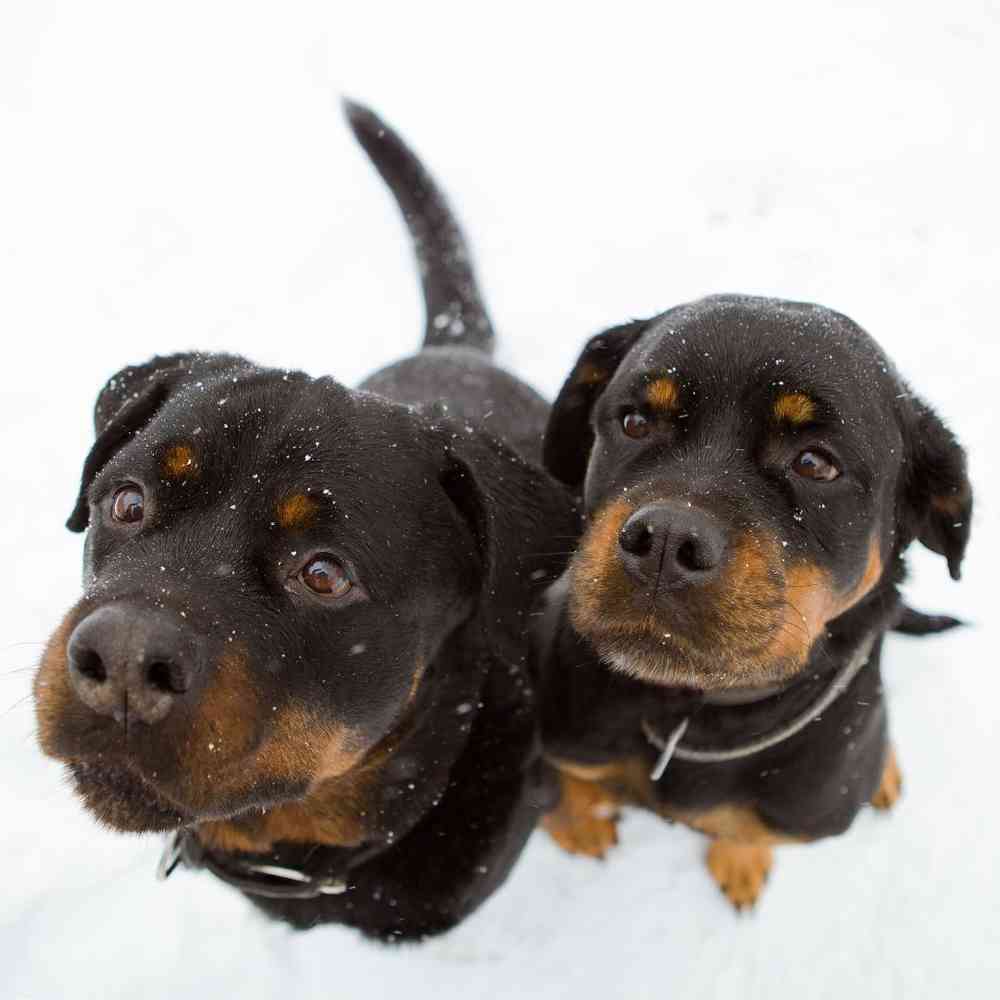

The Rottweiler is a robust working breed of great strength descended from the mastiffs of the Roman legions. A gentle playmate and protector within the family circle, the Rottie observes the outside world with a self-assured aloofness.


Want to know more about Rottweiler ?
Breed Traits
Clubs, Registries & Associations
American Canine Association Continental Kennel Club Universal Kennel Club International American Kennel Club United All Breed Registry America's Pet Registry, Inc. United Kennel Club (Based on breed recognition. See store for details on this particular puppy.)
Group
Heritage
Personality
Exercise/Energy Level
Additional Information
General Appearance
The ideal Rottweiler is a medium large, robust and powerful dog, black with clearly defined rust markings. His compact and substantial build denotes great strength, agility and endurance. Dogs are characteristically more massive throughout with larger frame and heavier bone than bitches. Bitches are distinctly feminine, but without weakness of substance or structure.
Head
Neck, Topline, Body
Forequarters
Hindquarters
Coat
Color
Gait
Temperament
Disqualifications
Description
Some assert there is a German Rottweiler and an American Rottweiler. The German Rottweiler is thought to be shorter, more thickset and burly with a big block head. The American Rottweiler is thought to be taller and leggier without the block head. Arnold, a Rottweiler, is in the HBO series Entourage A Rottweiler was in the movie Lethal Weapon 3
About
A male Rottweiler will stand anywhere from 24 to 27 muscular inches at the shoulder; females run a bit smaller and lighter. The glistening, short black coat with smart rust markings add to the picture of imposing strength. A thickly muscled hindquarters powers the Rottie’s effortless trotting gait. A well-bred and properly raised Rottie will be calm and confident, courageous but not unduly aggressive. The aloof demeanor these world-class guardians present to outsiders belies the playfulness, and downright silliness, that endear Rotties to their loved ones. (No one told the Rottie he’s not a toy breed, so he is liable plop onto your lap for a cuddle.) Early training and socialization will harness a Rottie’s territorial instincts in a positive way.
History
Standard
Nutrition
Grooming
Exercise
Training
Health